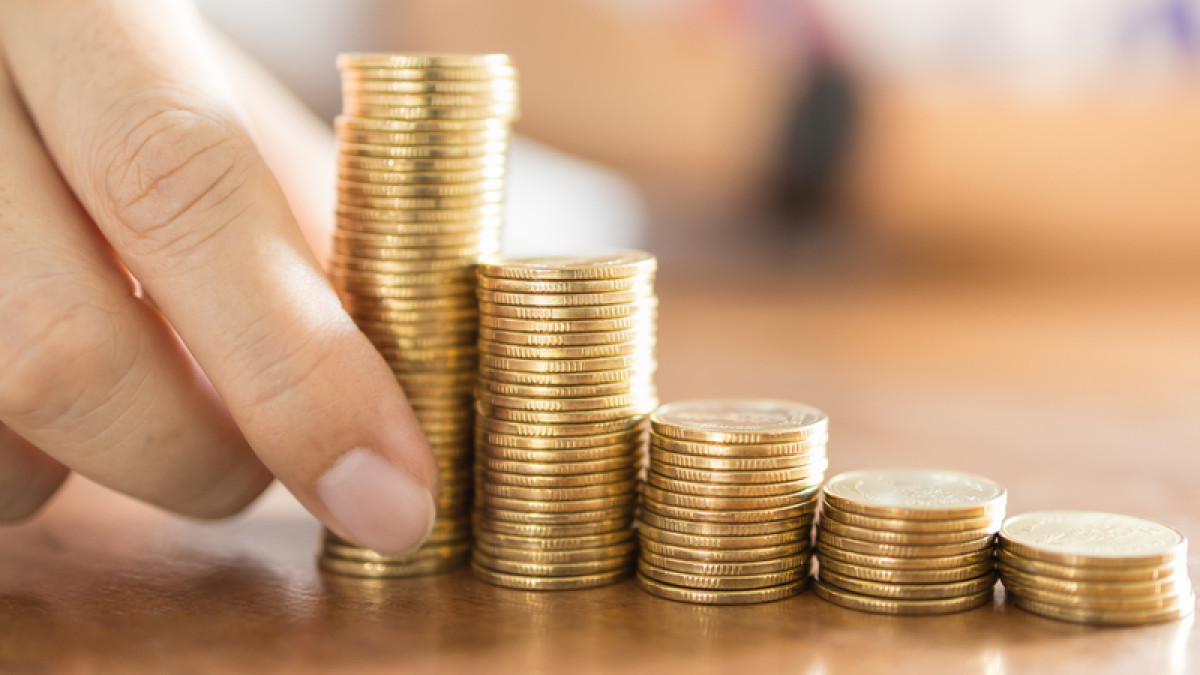
Retail customers invest in fixed deposits (FDs) for a fixed tenure – generally long-term – to earn high and assured returns. The funds deposited in fixed deposits are utilised to offer loans and advances to individual borrowers, companies, developers, etc. If borrowers with a large loan can not repay the loan, it leads to risk to depositors’ capital. Also, inefficient management of a financial institution may lead to insolvency.
In the interest of investors, banks provide insurance coverage with their fixed deposit accounts. It helps customers if any liquidity crisis occurs in the bank. Depositors need not panic about their funds invested in bank FDs.
Understanding Deposit Insurance
The deposit insurance model is like any simple medical insurance model where a third-party insurance company provides immediate funds when the insurance holder can not pay for medical expenses.
Similarly, the deposit insurance company provides bank deposits with insurance coverage. Considering bank FDs, when banks are scrutinised and the issue of fund mishandling is found, deposit insurance enables investors to withdraw funds on a priority basis.
Deposit Insurance for bank deposits in India is provided by the DICGC (Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the RBI (Reserve Bank of India). The deposit insurance entity ensures complete transparency and an unbiased approach towards all banking institutions.
A deposit insurance cover of Rs. 5 lakhs for each bank deposit account is provided by the DICGC. Each deposit account in banks is covered with insurance coverage. The government agency provides insurance coverage to all deposit accounts like savings, current, recurring and fixed deposits of all banks, including state, central, rural, cooperative and urban banks in India.
Crucial Roles of Deposit Insurance in FDs
The insurance provider for bank deposits must be government-owned due to the sheer amount of funds safety involved. A private or third-party institution might create transparency issues or stay biased without much authority over banks. A subsidiary arm of the RBI in India has the regulatory authority to control and manage the deposit insurance of all major banks. The deposit insurance entity, managed indirectly by the government, ensures complete transparency and an unbiased approach towards all banking institutions.
There are numerous reasons for the government and regulators to provide safety to depositors with an insurance plan. Below are some of the important roles played by deposit insurers to retain FD investors and facilitate a safe fixed deposit withdrawal after maturity.
– The Financial Safety System
The primary role of deposit insurance is stabilising the financial system if the bank fails to provide assured returns and pay back the deposited principal amount. Deposit insurance helps FD holders to access their insured funds immediately even if the bank fails. Thereby, it reduces their efforts to run to get back their funds.
– Prevent Panic Withdrawals
When a bank declares insolvency, it might trigger widespread fear among customers, especially FD investors, resulting in panic withdrawals. Deposit insurance plays a vital role to prevent unnecessary panic amongst depositors during times of crisis and ensure fixed deposit withdrawal after maturity.
– Includes Interest Earnings
The insurance provided by the DICGC covers a maximum of Rs. 5 lakhs per deposit account with banks in India. The deposit insurance also covers the interest earnings of the depositors. The DICGC’s deposit insurance includes coverage for the principal amount and interest also.
Fraudulent activities by institutions over the years have alerted banks and regulators to adopt insurance coverages for depositors’ safety. A liquidity crisis within the bank can spread serious panic among depositors since the institution might block or cap the withdrawals. All banks and institutions in the country’s ecosystem are interconnected and there are numerous reasons for the government and regulators to provide safety and stall the spread of the crisis over to other banks.
Conclusion
The central bank adopts appropriate methods to enhance the strength and efficiency of the financial system in India and stay active to cope with banking and liquidity crises.
The critical role of deposit insurance is to provide liquidity and stabilise the financial system. Even when a bank default or fails to return deposits to customers, customers can have immediate access to their deposited funds with a bank. Therefore, most investors prefer investing in FD accounts with reputed banks. Ultimately regulatory-insured deposit accounts enable financial safety across the banking system with complete transparency.
Read More Business Blogs:
Choose the Right In Car Fridge For Your Needs
Introduction to the Prefabrication method in Infra Industry: An Overview
To know more about keep reading Pinay Flix.